Causes of Earth Dam FailureReasons for Failure of Earth DamsOwners of dams and operating and maintenance personnel must be knowledgeable of the potential problems which can lead to failure of a dam. These people regularly view the structure and, therefore, need to be able to recognize potential problems so that failure can be avoided. If a problem is noted early enough, an engineer experienced in dam design, construction, and inspection can be contacted to recommend corrective measures, and such measures can be implemented. Acting promptly may avoid possible dam failure and the resulting catastrophic effect on downstream areaTypes of failure in Earth damsSince only superficial inspections of a dam can usually be made, it is imperative that owners and maintenance personnel be aware of the prominent types of failure and their telltale signs. Earth dam failures can be grouped into three general categories
A brief discussion of each type is as follows1. Over-topping Failures
Over topping failures result from the erosive action of water on the embankment. Erosion is due to un-controlled flow of water over, around, and adjacent to the dam. Earth embankments are not designed to be over-topped and therefore are particularly susceptible to erosion. Once erosion has begun during over-topping, it is almost impossible to stop. A well vegetated earth embankment may withstand limited over topping if its crest is level and water flows over the crest and down the face as an evenly distributed sheet without becoming concentrated. The owner should closely monitor the reservoir pool level during severe storms.
2. Seepage earth Failures
All earth dams have seepage resulting from water permeating slowly through the dam and its foundation. Seepage must be controlled in both velocity and quantity. If uncontrolled, it can progressively erode soil from the embankment or its foundation, resulting in rapid failure of the dam. Erosion of the soil begins at the downstream side of the embankment, either in the dam proper or the foundation, progressively works toward the reservoir, and eventually develops a direct connection to the reservoir. This phenomenon is known as "piping." Piping action can be recognized by an increased seepage flow rate, the discharge of muddy or discolored water, sinkholes on or near the embankment, or a whirlpool in the reservoir. Once a whirlpool (eddy) is observed on the reservoir surface, complete failure of the dam will probably follow in a matter of minutes. As with over topping, fully developed piping is virtually impossible to control and will likely cause failure. Seepage can cause slope failure by creating high pressures in the soil pores or by saturating the slope. The pressure of seepage within an embankment is difficult to determine without proper instrumentation. A slope which becomes saturated and develops slides may be showing signs of excessive seepage pressure.
3. Structural Failure of earthen damsStructural failures can occur in either the embankment or the appurtenances. Structural failure of a spillway, lake drain, or other appurtenance may lead to failure of the embankment. Cracking, settlement, and slides are the more common signs of structural failure of embankments. Large cracks in either an appurtenance or the embankment, major settlement, and major slides will require emergency measures to ensure safety, especially if these problems occur suddenly. If this type of situation occurs, the lake level should be lowered, the appropriate state and local authorities notified, and professional advice sought. If the observer is uncertain as to the seriousness of the problem, the Division of Water should be contacted immediately. The three types of failure previously described are often interrelated in a complex manner. For example, uncontrolled seepage may weaken the soil and lead to a structural failure. A structural failure may shorten the seepage path and lead to a piping failure. Surface erosion may result in structural failure.
Minor defects such as cracks in the embankment may be the first visual sign of a major problem which could lead to failure of the structure. The seriousness of all deficiencies should be evaluated by someone experienced in dam design and construction. A qualified professional engineer can recommend appropriate permanent remedial measures.
+ نوشته شده در پنجشنبه 21 مرداد1389ساعت 7:19 قبل از ظهر توسط سعید ناصری | نظر بدهید
Design of small Earth Dams
How to Design Small damsThe design below is suitable for dams up to 3m high. It is a uniform embankment of inorganic, clay loam soil, such as sandy clay loam, clay loam, silty clay loam, or soil with a higher clay content (sandy clay, clay, or silty clay). Any of these can be used provided cracks do not form. The dam must have a 'cut-off' which locks it into the subsoil foundation, ensuring that the dam is stable.A 3m high dam would typically have a 2m maximum depth of water when full, increasing to 2.5m under flood conditions, with a 0.5m depth of flow over the spillway. The top 0.5m (minimum) is required to provide a safety margin (free board) which allows for water rising on the dam due to wind and waves, and wear and tear on the dam crest. The total design height of the dam must be increased for construction by at least 10 per cent, to take account of settlement.How to Calculate height of a damThe height of the dam will depend on the storage required in the reservoir. To calculate this:
S = (R + AxE – Q) x T
The dam must be high enough to store this quantity of water. The storage capacity of the reservoir (C litres) is best determined from cross-section surveys across the valley, but can be estimated from the area of the reservoir (Am2) and the maximum depth of water at the dam (Dm) when full:
C = 330 A x D
The site should then be surveyed to estimate the area (A) of the reservoir for different values of D, and a trial-and-error method will then give the reservoir capacity (C) which meets the storage required (S) and provides a safety margin. The resulting value of A should then be used in the calculation of S to obtain a consistent result.
Height of dam = D + 1m
+ نوشته شده در پنجشنبه 21 مرداد1389ساعت 7:11 قبل از ظهر توسط سعید ناصری | نظر بدهید
بزودی...
بزودی . . .دی وی دی دستیار عمران در ۳ پک.
۱.civil assistant (دستیار عمران;کارشناسی)
۲.MS assistant (دستیار ارشد)
۳.projedt assistant (دستیار پروژه)
* کاری از دپارتمان عمران; مهندس ناصری , مهندس زاهدی نژاد
* با حمایت شرکت نیکا سازه
* مورد تایید اساتید دانشگاه
+ نوشته شده در پنجشنبه 21 مرداد1389ساعت 6:12 قبل از ظهر توسط سعید ناصری | نظر بدهید
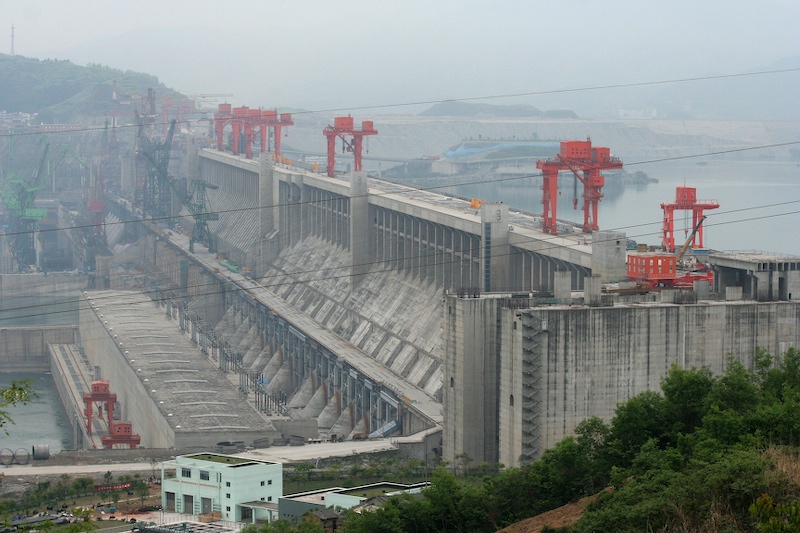
بزرگترین سد دنیا
بزرگترین سد دنیا روی رودخانه یانگ تسه کیانگ
سد سه دره (Three Gorges Dam) سدی هیدروالکترونیکی اسن که بر روی رودخانه یانگ تسه کیانگ در چین در حال احداث است و بزرگترین سد دنیاست .
در اینجا بزرگترین توربین های آبی برای تولید برق در دنیا احداث می گردد . به جز جرثقیلی که کشتیها را از این سوی سد به آن سوی سد منتقل می کند ، سایر بخشهای این سد بزرگ در تاریخ 30 اکتبر سال 2008 راه اندازی شد و این راه اندازی با به راه افتادن بیست و ششمین ژنراتور تولید برق این سد تکمیل شد . شش ژنراتور برق دیگر که قرار است ساخته شود همزمان با جرثقیل در سال 2012 به بهره برداری می رسد .
* در این پروژه قریب 28 میلیون مترمکعب بتن به کار رفته است .
* برای استحکام این پروژه نزدیک پانصد هزار تن فولاد در این سد بکارگیری شده است . که با آن میتوان برجی به اندازه 63 برابر برج ایفل بنا کرد .
* برای ساخت این سد قریب 110 میلیون متر مکعب خاک جابجا گردیده است .
* این پروژه با هزینه یکصد و هشتاد میلیارد یوان ساخته شد ، قریب 20 میلیارد یوان کمتر از پیش بینی 203 میلیار یوانی که هنگام ساخت پیش بینی شده بود .
* با ساخت این سد ارتفاع آب رودخانه یانگ تسه کیانگ بیش از 300 متر افزایش یافت .
* نیروگاه این سد هم اکنون قریب 23 هزار مگا وات برق تولید می کند (23 برابر نیروگاه اتمی بوشهر و 11 برابر سد کارون 3)
* ضخامت این سد در پایین 115 متر و در بالای آن 40 متر است .
* دواره بتنی این سد 2309 متر عرض و 101 متر ارتفاع دارد .
+ نوشته شده در دوشنبه 16 فروردین1389ساعت 11:33 قبل از ظهر توسط سعید ناصری | نظر بدهید
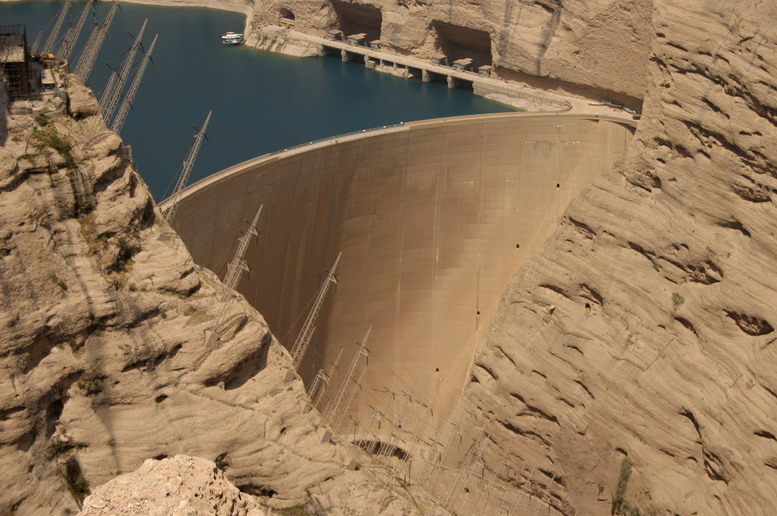
سد دز
سد دز یک سد بتُنی برقآبی است که در دوران سلطنت محمدرضا شاه پهلوی بر روی رودخانه دز توسط یک کنسرسیوم ایتالیایی در استان خوزستان و شهرستان اندیمشک احداث شد. اين سد ۱۲۵۰۰۰ هكتار از اراضی پايين دست را آبياری میكند و نقش مهمی در كنترل سيلاب های بالادستش دارد. نيروگاه این سد دارای قدرت نصب ۵۲۰ مگا وات میباشد. احداث سد عظیم دز، در سال ۱۳۳۶ خورشیدی توسط ایتالیاییها در کوههای زاگرس آغاز و در سال ۱۳۴۱ خورشیدی پایان یافت. این سد بتنی در ۲۳ کیلومتری شمال اندیمشک در شمال خوزستان واقع شده است. دریاچهای این سد ۶۵ کیلومترمربع مساحت داشته و گنجایش نهایی آن ۳.۳ میلیارد مترمکعب میباشد.[۲] بر روی رودخانه دز . این سد با ارتفاع ۲۰۳ متر در زمان ساخت خود به عنوان یکی از مرتفع ترین سدهای جهان (ششمین سد جهان در آن زمان) شناخته میشد و در حال حاضر نیز پنجاهمین سد بلند دنیا در بین سدهای ساخته شده و در دست ساخت میباشد. در سالهای اخیر پژوهشهای میدانی برای علاجبخشی این سد آغاز شدهاست. برای دراز مدت هم ساخت سد بختیاری که از بلندترین سدهای بتنی دو قوسی جهان خواهد بود در دردست مطالعه بوده و به زودی اجرا خواهد شد. چون حجم رسوبات پشت بدنه به حدی بالا آمده که در آینده نزدیک نیروگاه را از لحاظ اقتصادی خارج خواهد کرد. و چون قول دادم تاپیک ها رو انگلیسی بنویسم. The Dez Dam :is a large hydroelectric dam built in Iran in 1963 by an Italian consortium. The dam is on the Dez River in the Northwestern province of Khuzestan, the closest city being Andimeshk. It is 203 metres high, making it one of the highest in the world, and has a reservoir capacity of 3,340 million cubic meters. At the time of construction the Dez Dam was Iran's biggest development project. It is also possible to visit powerhouse which is located at the east side of the dam in the mountains. The powerhouse has eight vertical Francis turbines. The dam's current problem is the annual loss of reservoir capacity due to the erosion of soil in upstream areas. It has no educated engineers to remove sludge and clean the lake .on regular basis
+ نوشته شده در شنبه 30 آبان1388ساعت 11:33 بعد از ظهر توسط سعید ناصری | نظر بدهید
سد بتنی هوور
سعی میکنم از این تاپیک مطالب تخصصی رو بصورت انگلیسی بنویسم و این اولیش.
Hoover Dam, once known as Boulder Dam, is a concrete arch-gravity dam in the Black Canyon of the Colorado River, on the border between the U.S. states of Arizona and Nevada. When completed in 1936, it was both the world's largest electric-power generating station and the world's largest concrete structure. It was surpassed in both these respects by the Grand Coulee Dam in 1945. It is currently the world's 35th-largest hydroelectric generating station.
This dam, located 30 mi (48 km) southeast of Las Vegas, Nevada, is named after Herbert Hoover, who played an instrumental role in its construction, first as the Secretary of Commerce, and then later, as the President of the United States. Construction began in 1931, and was completed in 1936, more than two years ahead of schedule. The dam and the power plant are operated by the Bureau of Reclamation of the U.S. Department of the Interior. Listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1981, Hoover Dam was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1985.3.5]Lake Mead is the reservoir created by the dam, named after Elwood Mead, who oversaw the construction of the dam.دانلود فیلم سد بتنی هوور

+ نوشته شده در شنبه 30 آبان1388ساعت 9:57 بعد از ظهر توسط سعید ناصری | نظر بدهید
رشته ی سازه های هیدرولیکی
تو این پست می خوام راجع به دروس تخصصی و اختیاری این رشته براتون صحبت کنم.هر دانشجوی کارشناسی ارشد برای فراغت از تحصیل باید ۲۴ واحد تئوری و ۲ واحد سمینار و ۶ واحد پایان نامه رو بگذرونه که جمعا میشه ۳۲ واحد. البته با توجه به نوع دانشگاه ممکنه این مقادیر تغییر کنه. مثلا دانشگاه تهران اصلا واحد سمینار نداره!
از بین واحدهای تئوری هر دانشجو ملزم به گذروندن تمامی واحدهای الزامیه. و بقیه رو هم باید از بین واحدهای اختیاری انتخاب کنه.
دروس الزامی:
-ریاضیات مهندسی پیشرفته
- هیدرولیک پیشرفته
- روش اجزای محدود
-طراحی هیدرولیکی سازه ها (البته بیشتر مربوط به سازه های جانبی سد)
-یکی از دو درس زیر به اختیار (الزامی انتخابی)
-سدهای خاک - سدهای بتنی
البته باید گفت که انتخاب از میان دو درس بالا اون قدرا هم اختیاری نیست و بستگی داره که دانشکده امکان برگذاری کدوم یک از کلاس های " سدهای خاکی" یا " سدهای بتنی" رو داشته باشه. البته میتونید در صورت امکان برگذاری هر دو واحد یکی رو به عنوان الزامی و دیگری رو به عنوان اختیاری انتخاب کنید.
دروس اختیاری هم ممکنه با توجه به کلاسهای قابل ارائه از طرف دانشکده در بین دانشگاه های مختلف تفاوت داشته باشه. اما برای مثال دروس اختیاری دانشگاه علم و صنعت طبق موارد زیر هستند:
-آبهای زیر زمینی
-مهندسی رودخانه
-مدلهای هیدرولیکی
-مکانیک سنگ
-زمین شناسی مهندسی پیشرفته
-تئوری الاستیسیته و پلاستیسیته
-هیدرودینامیک
-دینامیک سازه ها
-هیدرولیک محاسباتی
-نیروگاه آبی
-تکنولوژی عالی بتن
-مهندسی پی پیشرفته
-بهینه سازی در مهندسی عمران
-هیدرولوژی مهندسی پیشرفته
-دینامیک سیالات پیشرفته
-مهندسی زلزله
- مهندسی سواحل
-اصول مهندسی بنادر
-مهندسی تونل
-اندرکنش آب-سازه
-تئوری صفحات و پوسته ها
-روشهای عددی در مهندسی آب
-اصول طراحی سازه های دریایی
-مبانی هیدرولیک دریا
*************
همون طور که میبینید رشته سازه های هیدرولیکی تنوع رشته ای زیادی از لحاظ دروس اختیاری داره. ولی باز هم برمیگرده به کلاس هایی که دانشکده برگزار میکنه و ممکنه شرایطی پیش بیاد که اصلا حق انتخاب نداشته باشید.
دوست عزیز، به سایت علمی نخبگان جوان خوش آمدید
مشاهده این پیام به این معنی است که شما در سایت عضو نیستید، لطفا در صورت تمایل جهت عضویت در سایت علمی نخبگان جوان اینجا کلیک کنید.
توجه داشته باشید، در صورتی که عضو سایت نباشید نمی توانید از تمامی امکانات و خدمات سایت استفاده کنید.







.jpg)






 پاسخ با نقل قول
پاسخ با نقل قول



علاقه مندی ها (Bookmarks)